IoT and Digital Infrastructures
by Jan Mahler

The way people communicate has always been subject to constant change. Starting with the development of language, writing, or modern technologies such as telegrams or telecommunications, we have always managed to come up with new ways to simplify and accelerate the exchange of information. With the beginning of the digital age and, above all, because of the Internet, one of the greatest milestones in interpersonal communication to date has been achieved: the ability to exchange information in real time.
For the past few years, a completely new buzzword has had a breakthrough: The Internet of Things (IoT). The term “IoT” describes the network of physical devices and other items which are enabled to connect, collect and exchange data. With the emergence of intelligent devices, communication no longer takes place among people only, but between devices, which we use in everyday life. According to a recent study, the number of devices connected to the IoT is expected to exceed 50 billion by 2022. Some therefore quite accurately describe IoT as the ‘Internet of Everything’.
Digital Infrastructures – The Achilles’ Heel of Digitization
The basic idea of IoT is simple. It is about connecting devices over the Internet and enabling them to communicate with us, with each other or with specific applications. As the number of devices communicating with each other increases, so does the amount of data that is generated and circulated as part of this communication. Complexity is created by the amount of data, but also by the large number of different devices that transmit data. This leads to a greater demand for IT infrastructures and data centres. For data to be properly collected, transmitted and evaluated in real time, factors such as computing power, the provision of direct and secure connections in data centres, as well as mapping these global interdependences are becoming more important.
| Structural Challenges for Implementing IoT | |
| • | Integration into existing IT (including the availability of hybrid cloud models) and access to adjoining IoT ecosystems |
| • | The provision and processing of data where it is needed |
| • | Leveraging data content |
| • | Guaranteed data security despite global availability |
| • | Speed (latency, scaling, adaptation) |
The expectations placed on the underlying IT infrastructure are very high: it must be both scalable and able to handle a significant amount of data. Considering the enormous increase in data that travels across the Internet every second, the Internet will soon have to evolve.
„For companies that rely on IoT, it is not only important how quickly and reliably they connect to market participants, but also how flexible this interaction can be.“
Interconnection offers the basis for such an evolution. Interconnection can be understood as a ‘second Internet’ based on direct, private connections between many different market participants, such as companies, technology providers, IT service providers and their partners. Interconnection creates physical connections between servers of individual actors in a neutral environment, such as the data centre. This allows participants from the same ecosystem to connect across short distances and exchange information with other participants quickly and reliably –without failures and at very low latency. This concept guarantees a high level of security, in particular with regard to digital payment methods based on apps or online accounts.
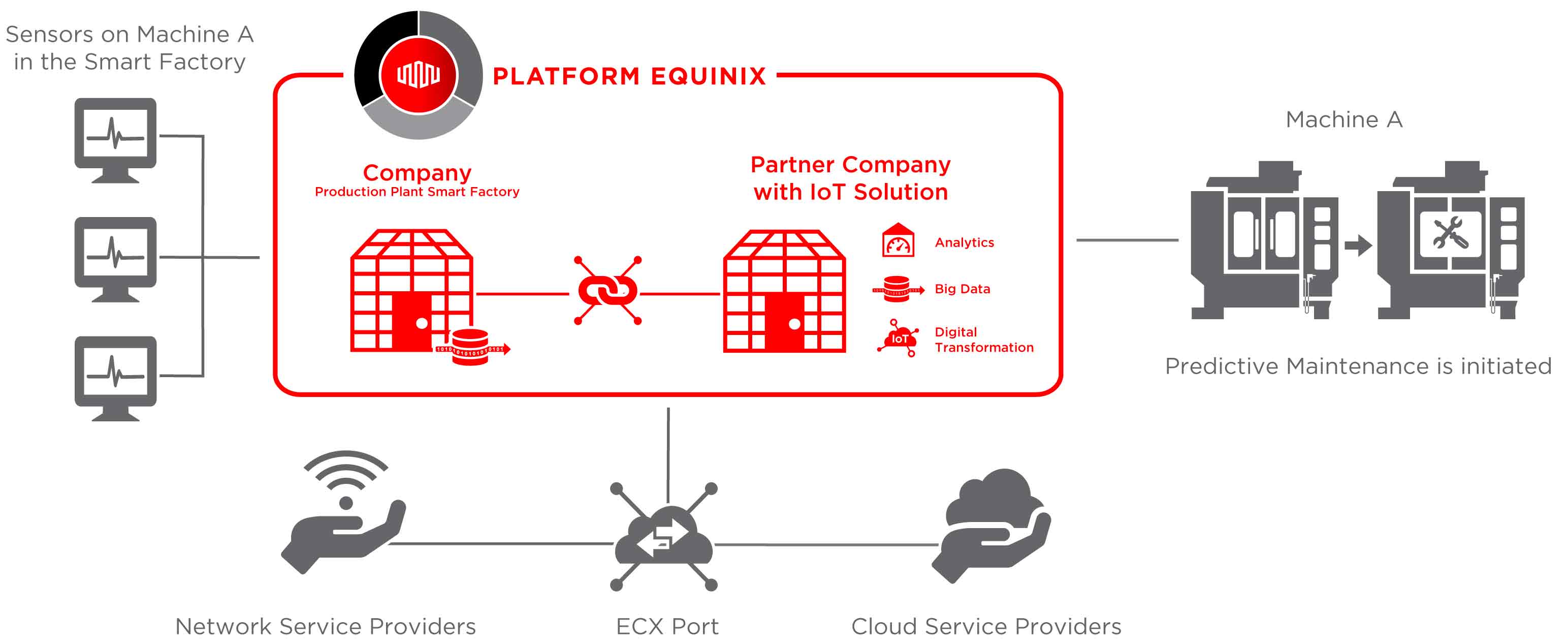
For companies that rely on IoT, it is not only important how quickly and reliably they connect to market participants, but also how flexible this interaction can be. If there is a large demand for storage space, computing power or connections, for example, new capacities can be added and expanded via cloud services, regardless of the location. However, setting up and maintaining such dynamic IT infrastructures is challenging for many companies. Therefore, companies are increasingly outsourcing their IT infrastructures to data centres and rely on the expertise of external providers. This approach is not only faster and more flexible, but also more cost effective than setting up own IT infrastructures.
“The path from raw data to actual business value begins with data collection, followed by data analysis that helps identify patterns and ends with the distribution to relevant parties, who use this information and the insights gained from it for their business operations. Equinix IT infrastructure solutions are involved in each of these steps along the value chain and thus act as enablers. They build a bridge between the potential of IoT and the necessary foundation to fully exploit this potential across all areas of application.”
– Donald Badoux, Managing Director of Equinix in Germany –
IoT and Production – Industry 4.0
IoT holds tremendous potential. In the eyes of the economy, IoT is a promising area from which companies expect to generate massive revenue. The data obtained can be used profitably in a variety of ways. When it comes to IoT applications in production, for example, the term Industry 4.0 is often used. It refers to applications based on the core functions of analytics and IoT to automate processes and optimize efficiency in the production and maintenance of machines and systems.
One example of Industry 4.0 is the automatic evaluation of data to optimize maintenance cycles, also known as ‘predictive maintenance’. Intelligent sensors collect data, which is evaluated to provide insights into the point in time when certain machine components used in production require repair or even replacement.
Automatic data evaluation helps to reduce the energy required to heat or cool machines and thus contributes to an increase in productivity and capacity utilization. Other benefits include optimized operating procedures and lower costs. Automatic data analysis also helps to understand customer behaviour and their preferences. This allows companies to better adapt their business models and offers to their respective target groups. From an entrepreneurial perspective, IoT thus also offers the key to honing one’s competitive edge.
| Advantages of IoT at a Glance | |
| • | IoT as a base technology for the development of new business models and products (innovation) |
| • | Increased sales through improvement of existing products and services |
| • | Reduced downtime and production costs |
| • | Flexible production processes and rapid adaptation to changing requirements |
| • | Better monitoring through real time sensor data and a comprehensive overview of the status of production processes |
High data transfer rates and effective broadband connections are the basis for the successful integration of IoT into existing processes. High latency times or even data access failures can have a detrimental impact on businesses. Especially in the context of Industry 4.0, more and more companies require an underlying infrastructure that is fast and delivers high performance while minimizing downtimes and providing quick access to backups in the event of a critical failure.
IoT as Growth Engine
Digital transformation will fundamentally change the way value can be created in the so-called Fourth Industrial Revolution. Classical factors and rules of corporate development, such as company size, stability and long-term growth, which were up until now indicators of success or failure, will lose importance in the coming years. Instead, it is becoming increasingly important for companies to question existing models and to take advantage of current and future technological opportunities when implementing new, digital business models. In a constantly changing technological environment, the extent to which companies can flexibly adapt will become critical to their success.
Companies must not only have the appropriate know-how and a high degree of flexibility, but they also need to make fundamental strategic decisions as to how and for what purpose IoT should be implemented. Whereas today, IoT solutions are mainly used for process optimization, in the future it will also play a vital role in developing new products and services and in doing so drive revenue growth. Once goals have been determined, individual IT solutions from partners can help to lay the respective foundation – that is the most suitable infrastructure.
„Whereas today, IoT solutions are mainly used for process optimization, in the future it will also play a vital role in developing new products and services and in doing so drive revenue growth.“
Small companies and start-ups in particular have an advantage here. They are generally able to adapt new technologies faster than large corporations or medium-sized companies. The latter are limited in their flexibility as they take the risk of burdening their own existing sales through change and restructuring measures. Yet despite this inherent risk, digitization offers opportunities for companies of any size. Especially medium-sized companies have the potential to benefit from IoT platforms. It is important that small and medium-sized enterprises do not lose sight of this unique opportunity and invest in the use of IoT at an early stage.//
For a German version of this article, please click here
| Der Text ist unter der Lizenz CC BY-SA 3.0 DE verfügbar. Lizenzbestimmungen: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/de/ |

 Handbuch Künstliche Intelligenz
Handbuch Künstliche Intelligenz Handbuch Digitalisierung
Handbuch Digitalisierung  Handbuch Handel mit Zukunft
Handbuch Handel mit Zukunft Handbuch HR-Management
Handbuch HR-Management Handbuch Digitalisierung
Handbuch Digitalisierung



